Visualizations grab attention, but the true Power lies in your Data model. Data modelling in Power BI empowers efficient data management and agile analytics, setting a strong foundation for impactful reporting and insightful decision-making.
1. Types of Tables
The main building blocks of every data model are tables. In Power BI, we distinguish between two types of tables: Fact tables and Dimension tables.
Fact table
Stores data like quantity sold, sales value, etc. Example: Sales fact table with facts and IDs linking to dimensions.
Dimension table
Dimensions are lookup tables with an ID as primary key and extra info. Example: Product dimension.

2. Types of Relationships
On the other hand, Relationships are key connectors in your Power BI data model. In Power BI, we distinguish between three main types of relationships: One-to-Many, One-to-One, and Many-to-Many.
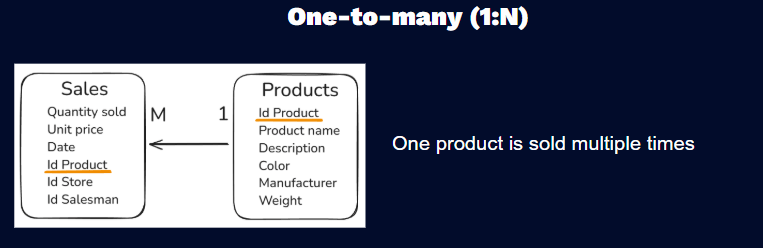
One to Many (1:M)
Connects a single unique record in one table to multiple related records in another. Always used for connection Dimension (on the side of ,,One”) to Fact table (on the side of ,,Many”).
Eg. One product from Dimension is sold multiple times in Fact table
Many to Many (M:N)
Occurs when multiple records in one table relate to multiple records in another, often managed with a bridge table.
Eg. Products in stores represents M:N relationship

One to One (1:1)
Connects a single unique record in one table to multiple related records in another. Try to Join both tables into 1 to simplify a Data model.
3. Types of Data models
Data models shape how efficiently you analyze your data. In Power BI, you typically choose between a Star schema and Snowflake schema.
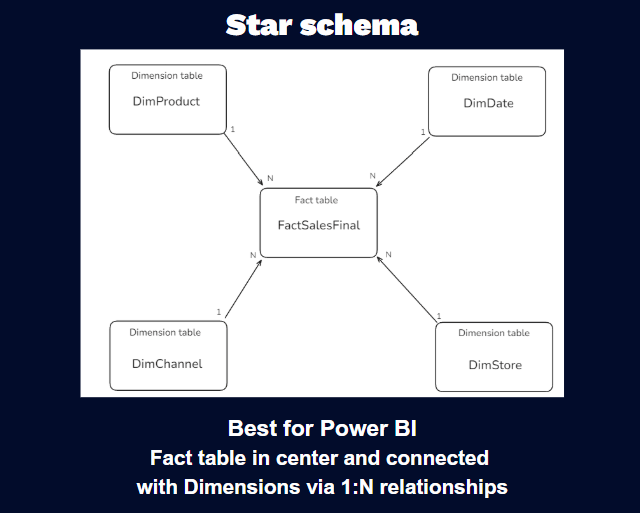
Star schema
A star schema features a central fact table directly connected to dimension tables. This structure offers simpler queries and faster performance.
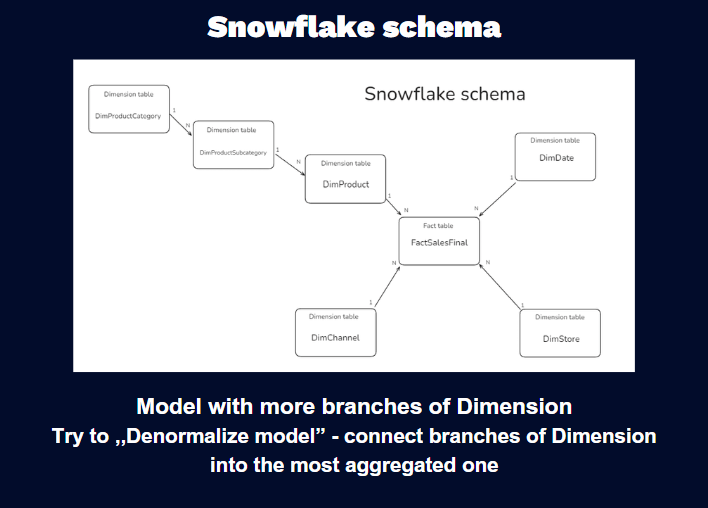
Snowflake schema
A snowflake schema normalizes dimensions into multiple related tables, reducing redundancy at the cost of added query complexity.
In conclusion, selecting the right data model in Power BI—whether it’s a Star schema for simplicity or a Snowflake schema for enhanced normalization—is essential for unlocking seamless data integration and optimal performance.
By embracing best practices and aligning your schema design with business needs, you ensure your data models are both efficient and scalable. This approach empowers you to build powerful, flexible analytics solutions that drive smarter business outcomes.
