Power BI visuals are great, but the real power comes from the data behind them. Connecting Dataverse to Power BI unlocks deeper insights, enabling real-time analytics and smarter decision-making.
There are 3 ways, how we can connect Dataverse to Power BI:
1. Connecting via Native connector
Connecting via the native connector is the simplest and most straightforward option. This type of connection supports both Import and DirectQuery mode for real-time insights.
The process is simple:
In Power BI Desktop, select a new data source -> Dataverse
Authentication is done through a Microsoft account (Microsoft OAuth 2.0)
Then, just choose the Dataverse environment and the tables you want to load into Power BI

Pros of Dataverse native connector:
Very easy and straightforward setup
Option to load data using Import or DirectQuery mode
Cons of Dataverse native connector:
All data transformations must be done in Power Query
2. Connecting via REST API
Connecting via REST API is the most complex method for bringing data into Power BI. It requires handling the Dataverse REST API limitations, which return only 5,000 records per API call. To retrieve all data from a table, a paginated loading approach must be implemented.
Steps to connect Dataverse to Power BI via REST API:
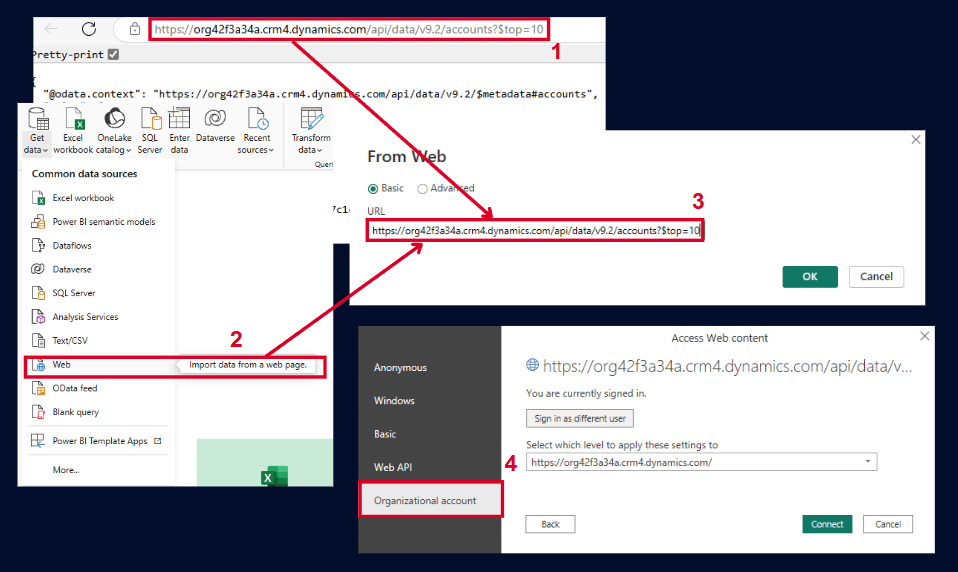
In Power BI Desktop, select Web as the data source
Use the following HTTP request:
"https://DataverseEnvironmentId/api/data/v9.2/EntityLogicalName"Authentication is done through a Microsoft account (Microsoft OAuth 2.0)
The HTTP request can include filters, select statements, etc., to refine the data

Pros:
Ability to retrieve only the necessary data without using Power Query
Cons:
Complex setup
Requires advanced knowledge of Dataverse API
API call limit of 5,000 records per request
3. Connecting to Dataverse SQL Database
Now comes what I consider the best option—connecting directly to the Dataverse SQL Database. This method allows filtering, renaming, and selecting columns right at the source. Additionally, it supports standard SQL Server functionalities like DirectQuery and Import mode. This means you can load only the necessary data into Power BI while still enabling real-time insights via DirectQuery mode.
Setup Instructions:
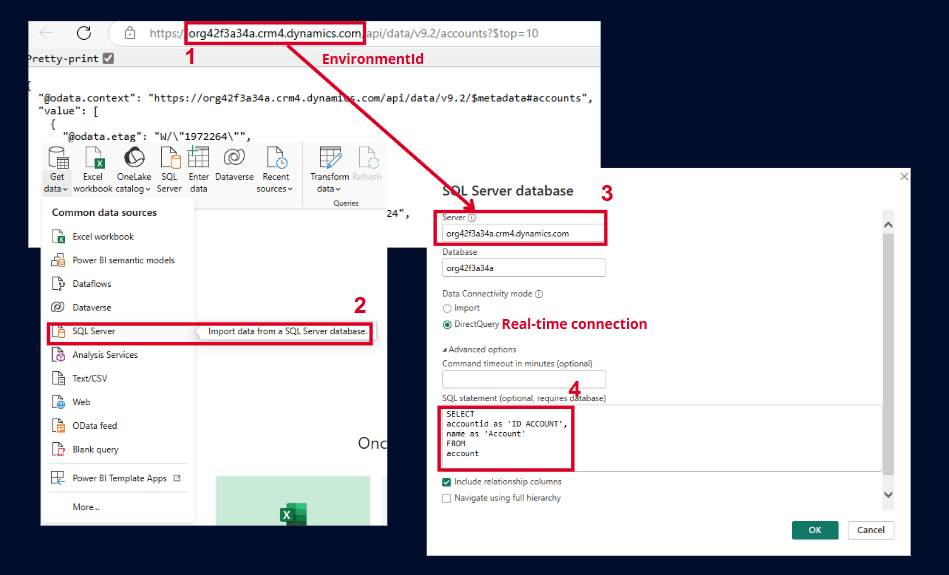
In Power BI Desktop, select SQL Server as the data source
The SQL Server name is the Dataverse environment URL, and the database name is DataverseEnvironmentId
You can write a standard T-SQL SELECT statement to define the data retrieval
Pros:
Supports both Import and DirectQuery mode
Ability to select and rename columns directly at the source
Simple setup for users familiar with SQL
Cons:
Slightly more complex setup compared to the native connector
Conclusion
In conclusion, connecting Dataverse to Power BI unlocks powerful analytics and real-time insights.
By choosing the right connection method—whether the native connector, REST API, or direct SQL access—you ensure efficient data retrieval and seamless integration. Optimizing your setup allows you to build dynamic, data-driven reports that support smarter decision-making and business growth.
