Automatic DAX documentation transforms your BI workflow by generating complete, clear documentation of your DAX queries and measures. It automatically records all key logic and dependencies, cutting down manual work and ensuring transparency.

INFO DAX
The Automatic Semantic Model is built on top of the Open AI API and INFO DAX. The INFO DAX function lists all DAX functions, and the Open AI API does the magic by automatically generating definitions for each DAX function.
You can test INFO DAX in the DAX query view tab in the Power BI Desktop

DAX Code:
EVALUATE
VAR _measures =
SELECTCOLUMNS(
INFO.MEASURES(),
"Desc", [Description],
"TableID", [TableID],
"DAX Formula", [Expression]
)
VAR _tables =
SELECTCOLUMNS(
INFO.TABLES(),
"Table ID", [ID],
"Table Name", [Name]
)
VAR _combined =
NATURALLEFTOUTERJOIN(_measures, _tables)
RETURN
SELECTCOLUMNS(
_combined,
"Desc", [Desc],
"Measure", [DAX Formula],
"Home Table", [Table Name]
)
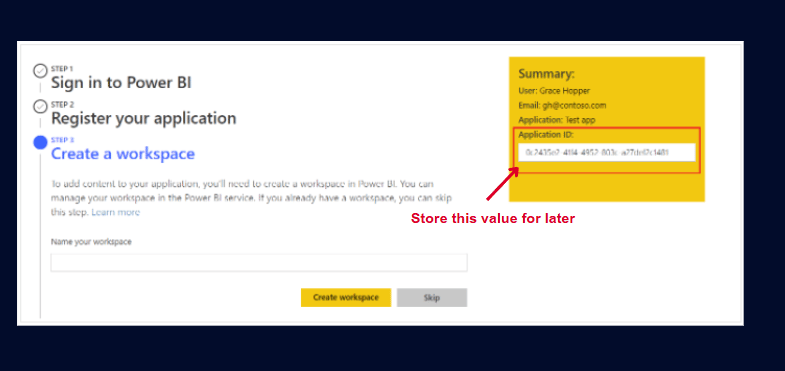
1. Register Power BI app
First, you need to register a Power BI app to call the Power BI API and obtain all metadata from the Power BI semantic model.
You can register your Power BI app at:
Then can choose between creating an app for your customer or your organization. I recommend choosing your organization:


Then choose the Power BI app permissions by clicking on all of the 'Read' permissions listed in the registration form.

And finally store the Application ID for later:
2. Open Power Query in new Documentation pbix file
We need to create several functions in Power Query:
GET Query – a function to retrieve data from DAX INFO for the defined semantic model.
ChatGPT Function – a function to call for each row of the documentation prompt.
GET Access Token – a function to obtain an access token for the Power BI API.
Paste these codes into the Power Query Editor as a Blank Query.
GET Query
(accessToken as text) =>
let
datasetId = "XXXXXXXXXXX", // DatasetId to be documented
dax = "EVALUATE VAR _measures = SELECTCOLUMNS( INFO.MEASURES(), \""Measure\"", [Name], \""Desc\"", [Description], \""DAX formula\"", [Expression], \""TableID\"", [TableID] ) VAR _tables = SELECTCOLUMNS( INFO.TABLES(), \""TableID\"", [ID], \""Table\"", [Name] ) VAR _combined = NATURALLEFTOUTERJOIN(_measures, _tables) RETURN SELECTCOLUMNS( _combined, \""Measure\"", [Measure], \""Desc\"", [Desc], \""DAX Formula\"", [DAX formula], \""Home Table\"", [Table] )",
body = "{
""queries"": [
{
""query"": """ & dax & """
}
],
""serializerSettings"": {
""includeNulls"": true
}
}",
bodyContent = Text.ToBinary(body),
Zdroj = Json.Document(Web.Contents("https://api.powerbi.com/v1.0/myorg/datasets/"&datasetId&"/executeQueries", [
Headers=[#"Content-Type"="application/json", Authorization="Bearer " & accessToken],
Content=bodyContent
])),
value = Zdroj[value]
in
Zdroj
GET Access Token
Replace:
username with your Entra ID account email
password with your Entra ID account password
clientId with your Application ID (from step 1)
() =>
let
username = "XXXXXXXXX", //AD account Email
password = "XXXXXXXXX", //AD account Password
clientId = "XXXXXXXXX", //Application client ID
body = "grant_type=password&resource=https://analysis.windows.net/powerbi/api&client_id="
& clientId
& "&username="
& username
& "&password="
& password,
Data = Json.Document(
Web.Contents(
"https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/token/",
[
Headers=[#"Content-type"="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"],
Content=Text.ToBinary(body)
]
)
),
access_token = Data[access_token]
in
access_token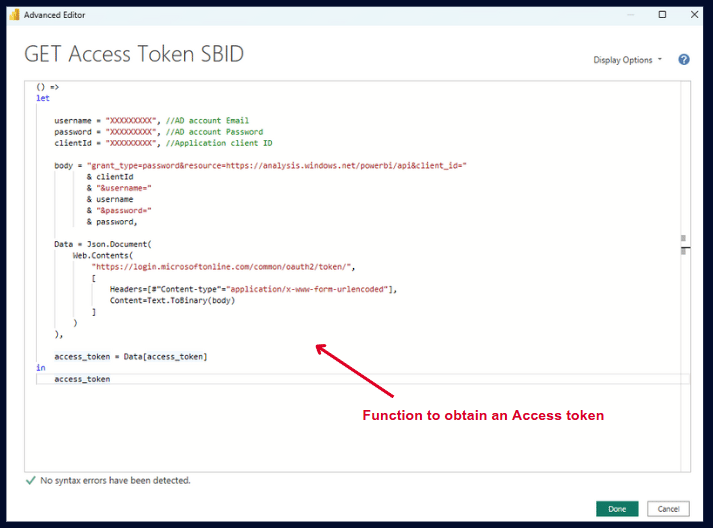
ChatGPT Function
(Later on, change the apiKey variable to the obtained Open AI API key.)
let
Output = (prompt as text) as text =>
let
url = "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
apiKey = "XXXXXXXXXXXXX", //Chat GPT API Key
headers = [
#"Content-Type" = "application/json",
#"Authorization" = "Bearer " & apiKey
],
body = Json.FromValue([model = "gpt-3.5-turbo", messages = {[role="user", content = prompt]}]),
response = Web.Contents(url, [Headers=headers, Content=body]),
content = Json.Document(response)[choices]{0}[message][content]
in
content
in
Output
3. Chat GPT API Key
Now you need to obtain your ChatGPT API key from:
https://platform.openai.com/
Then navigate to API Keys → Create New Secret Key, copy it, and store it for later use.

4. Now the Fun with Documentation Begins!
Copy and paste the following query into the Power Query Editor:
let
// Combine source retrieval and initial transformations.
AccessToken = #"GET Access Token"(),
BaseTable = Table.RenameColumns(
#table(1, {{AccessToken}}),
{"Column1", "AccessToken"}
),
// Inline custom function and retrieve data in fewer steps.
QueryResult = Table.AddColumn(
BaseTable,
"GET Query",
each #"GET Query"([AccessToken])
){0}[GET Query][results]{0}[tables]{0}[rows],
FinalTable = Table.FromList(
QueryResult,
Splitter.SplitByNothing(),
null,
null,
ExtraValues.Error
),
ExpandedTable = Table.ExpandRecordColumn(
FinalTable,
"Column1",
{"[Measure]", "[Desc]", "[DAX Formula]", "[Home Table]"},
{"[Measure]", "[Desc]", "[DAX Formula]", "[Home Table]"}
),
// Apply the final custom function directly.
CustomFunctionApplied = Table.AddColumn(
ExpandedTable,
"[Chat GPT Definition]",
each #"ChatGPT Function"(
"Measure definition: " &
[#"[DAX Formula]"] &
", Write me a quick description of this measure. Then list all referenced Columns and Measures in this DAX Formula."
)
)
in
CustomFunctionAppliedApplied Steps:
Step 1: Obtaining the AccessToken

Step 3: Expanding the records.

Step 4: Applying the Open AI API function to automatically generate documentation.

Voilá!
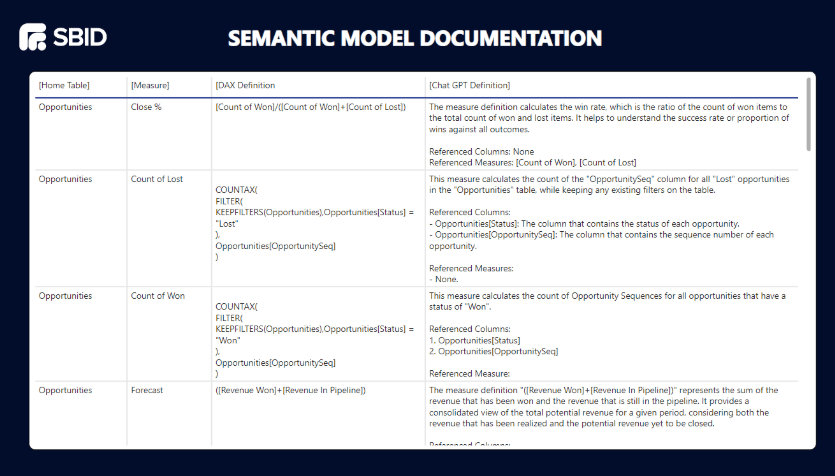
Automatic DAX documentation streamlines your BI workflow by capturing detailed logic and dependencies without manual effort.
By automating these steps, you simplify complex calculations and improve transparency. Mastering this approach opens up new possibilities for efficient collaboration and clearer insights in your data models.
